The Most Common Male Urological Problems That Can Be Treated
Various pathological processes in men can develop for a variety of reasons. The most common of them:
- genital infections
- nonspecific bacterial inflammatory processes;
- the development of tumors (benign or malignant);
- hormonal disorders;
- damage to nerves, blood vessels;
- injuries
- chemical poisoning;
- diseases of extragenital structures affecting the reproductive system.
The doctor’s task is to find out why the signs of male illness appeared, and conduct targeted treatment to eliminate the main etiological factor.
Penile Diseases
The main pathologies of the male penis include the following pathologies:
- Balanoposthitis
This is the most common disease which usually manifests itself in an acute form. This is an inflammatory process of the head of the penis which is most often caused by infection. Less commonly, autoimmune processes, allergies, injuries, and other factors become the cause. The head of the penis swells and blushes; plaques, rashes, erosive and ulcerative elements appear on it. To treat the disease, it is necessary to establish the pathogen and destroy it with drugs. After that, all the symptoms go away. Find more information on health portal: healthline.com/health/mens-health/balanoposthitis.

- Phimosis
The disease is characterized by a narrowing of the foreskin. It may be a consequence of the previous one. Due to inflammation, scarring of the skin occurs. Scar tissue stretches very badly. Therefore, the foreskin does not open the head. The disease requires surgical treatment. Otherwise, complications are possible. The most dangerous of them is paraphimosis which in fact is a consequence of violent attempts to open the head. It is infringed by constricted flesh, blood supply ceases. If timely assistance is not provided, tissue necrosis may occur.
- Peyronie’s disease
The disease is characteristic for older men. It manifests by the appearance of a solid fibrous plaque on the penis. It causes two significant problems: penis curvature and erection pain. Over time, erectile dysfunction may develop. The disease is treated surgically.
- Erectile dysfunction
This is not always a penile disease. Often it is caused by mental disorders, diabetes mellitus or hormonal disorders. But still, the most common cause is a violation of the blood supply to the penis. In addition, the function of this particular organ is lost, whatever the origin of the pathology. Erectile dysfunction usually develops in older men. In youth, psychogenic impotency is more common. It requires psychotherapy, so urologists can do little to help in such cases. In older men, an erection is disturbed as a result of atherosclerosis, nerve damage, and a decrease in testosterone in the blood. Most forms of pathology are treated in one way or another. With vascular erectile dysfunction, Viagra and drugs similar in mechanism of action are used. Viagra and its analogs are given extensive coverage on the Skyline Urology website if you would like to find out all about more professional approach to ED medicating. In case of hormone deficiency, replacement therapy is prescribed.
- Priapism
This term refers to an erection that is not associated with sexual arousal, lasts more than 4 hours and does not disappear after ejaculation. There are three forms of priapism:
- ischemic – it accounts for 95% of cases, this is the result of oxygen starvation of member tissues;
- non-ischemic – due to trauma that results in the formation of arteriolacunar fistula;
- recurrent – associated mainly with diseases of the nervous system.
In most cases, doctors have to deal with ischemic priapism. It can develop after drinking alcohol or drugs. Priapism is often found in cancer, as a result of compression of blood vessels by tumors. It is observed in every third patient with prostate or bladder cancer, in every tenth patient with kidney cancer. Less commonly, it occurs against a background of infectious diseases. The condition requires emergency medical attention. After 12 hours, irreversible changes begin in the cavernous tissue. If an erection lasts more than a day, erectile dysfunction after stopping priapism develops in 90% of patients.
Testes Diseases

There are a lot of diseases of testicles. But most of them, such as testicular torsion, abscess, cryptorchidism, traumatic injuries, tumors, etc. are rare. We will talk about two diseases that are detected most often.
- Varicocele
This is varicose veins of the spermatic cord. It leads to overheating of the scrotum. Varicocele may be complicated by infertility and testicular atrophy. According to different authors, varicocele is detected in 2-30% of all men. To the expansion of the veins there is a hereditary predisposition. But in most cases, the disease manifests itself in adulthood. The majority of patients with a newly established diagnosis are people from 15 to 30 years old. The higher the frequency of pathology among manual workers and athletes. Treatment is carried out by surgical methods. To date, many operations have been developed. The most popular areas are as follows:
- endovascular occlusion – the intervention is performed through the blood vessels;
- microsurgical interventions such as Marmara surgery;
- laparoscopic surgery.
Even today, more than 120 types of various operations are used. Their choice is determined by the preferences and skills of the doctor, as well as the peculiarity of the clinical situation. Varicocele is not always treated. Therapy is not required if:
- a man is sure that in the future he will not wish to conceive a child;
- no symptoms;
- there are no atrophic changes in the testicle.
In young men, surgery can be performed as soon as deviations in a semen analysis appear. But if they are not, observation is possible.
- Epididymitis and orchitis
These are inflammatory processes of the epididymis. Sometimes they extend to the testicle itself. The causes most often become infections:
- venereal diseases
- non-specific infectious processes
- systemic viral infections (most often mumps)
In case of STD infection, the infection enters the testicle in an ascending way, through the urethra and the ducts of the vas deferens. It is also possible the spread of bacteria through blood or lymph from other parts of the body, including those remote from the scrotum. For treatment, the identification of the pathogen and its destruction with antibiotics is required.
Prostate Diseases
There are three most common diseases of the male prostate gland. One of these pathologies occurs at a young age. Two more diseases develop mainly after 60 years.
- Prostatitis
Inflammation of the prostate is acute and chronic. Acute form is rare, but it is the most dangerous. The causative agent is Escherichia coli, less commonly, another gram-negative flora. Symptoms of this male disease appear suddenly. A man is concerned about pain in the perineum, fever, general deterioration in health. Complications are possible, the most dangerous of which are:
- acute urinary retention;
- prostate abscess.
Pathology is treated in a surgical or urological hospital. With urinary retention, catheterization of the bladder is done. In the case of an abscess, surgical intervention is necessary, but most patients are treated conservatively. Antibiotics are used to eradicate bacteria. Chronic prostatitis can have a different origin which is most often they infectious or congestive (stagnant). Inflammation of the prostate gland occurs with minimal symptoms. It can be caused by an undiagnosed on time sexually transmitted infection, nonspecific bacteria, as well as congestion in the prostate. Violation of the outflow of lymph and venous blood leads to edema. It can be triggered by obesity, low motor activity, a sedentary lifestyle, and an irregular sex life.
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia
It develops to one degree or another in all elderly men. The fight against this disease, once started, continues uninterrupted. It can only be completed with surgery. The essence of the pathology is that under the influence of the hormone dihydrotestosterone, the prostate overgrows gradually. It increases in volume. Over time, this leads to a violation of urodynamics. The prostate can squeeze urethra, ureters, and sometimes rectum. Most deaths by prostate adenoma are associated with compression of the ureters, which leads to the development of renal failure. At the initial stage, the disease is treated conservatively. An enzyme blocker that converts testosterone to dihydrotestosterone is used to slow down prostate growth. Alpha-blockers are used to reduce symptoms. These medicines are taken continuously.
Taking Drugs for Men’s Diseases
All other means can be used at the request of the doctor and patient: many of the drugs that you see in TV ads do not have clinically proven efficacy. But they favorably affect the psycho-emotional state of the patient and in most cases do not harm the body. At a certain stage, when the prostate becomes too large, you have to reduce it in one way or another. Minimally invasive procedures are used, during which excess tissue is destroyed by various energies (electric current, laser, etc.).
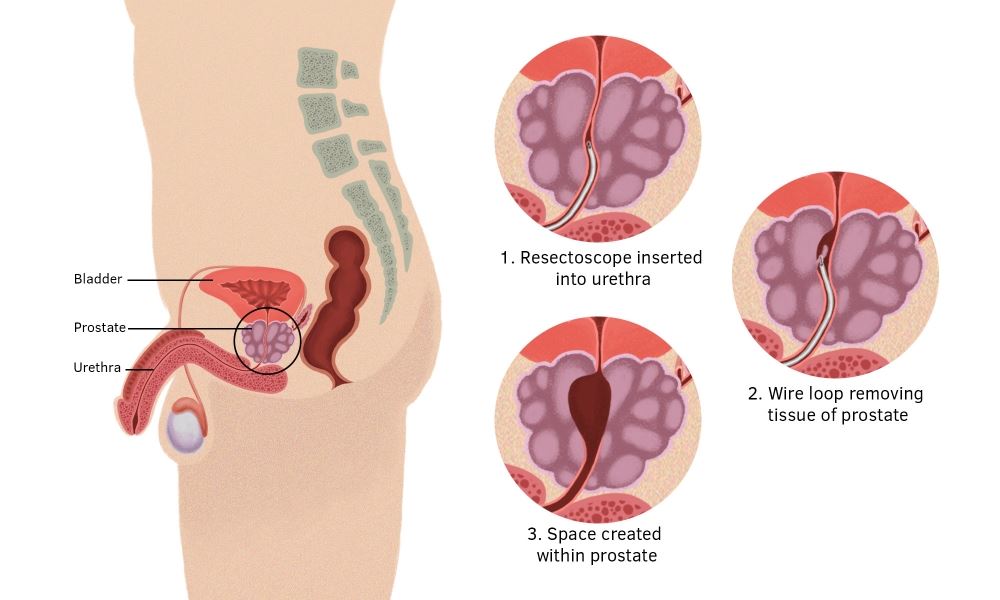
Operations are also performed, the most popular of which is transurethral resection of prostate. With a gland size of more than 90 cubic centimeters, either open surgery or laser holmium enucleation is indicated. The latter intervention is gentler, but more expensive. It requires special equipment and is not carried out in every clinic.
- Prostate Cancer
It takes fifth place in Canada among all oncological diseases. Among male tumors, it takes second place after lung cancer. This type of cancer is one of the most favorable in relation to malignant neoplasms. Significant successes have been achieved in treating the disease. In addition, the tumor itself in most cases is not too aggressive, grows slowly. Once diagnosed, even without treatment, most men will live for more than 10 years. Therefore, when detecting a neoplasm in elderly patients, observation tactics are often used.
Only if the disease begins to progress, measures are taken to treat it. To combat this disease, radical surgery to remove the prostate is used. Chemotherapy, hormonal and radiation therapy are applied. At the last stage, radionuclide methods are used. For learning more about precancerous conditions, check the article on Canadian Cancer Society website.
Male Infertility
About 15% of couples cannot conceive a child without medical assistance. Of these, 40% of cases reveal infertility in the spouse. There can be many reasons for this condition. Infertility is not a separate disease; it can be the result of many male diseases. The main reasons for occurrence of male infertility are as follows:
- Testicular disease
The most common cause of infertility in this group is varicocele. It also leads to orchitis, testicular torsion, genetic defects and developmental abnormalities, cryptorchidism. Sometimes testes are damaged as a result of trauma, radiation, chemotherapy. Hormonal disorders are also found. With a decrease in hormone-producing function of the testicles, hypergonadotropic hypogonadism is diagnosed.
- Diseases of the hypothalamic-pituitary system
The system regulates the function of the testicles. The most common problems are hyperprolactinemia (elevated levels of prolactin in the blood) or hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. The second disease is due to the fact that the pituitary gland does not produce enough substances that are needed to stimulate testicular function. Those do not work at full strength, which turns into a lack of testosterone.
- Post-testicular causes
These include diseases of the prostate and vas deferens. The causes may be genital infections, congenital or acquired obstruction of the epididymis. Even if the testicles produce good quality sperm and in sufficient volume, it is not always able to penetrate the urethra during ejaculation. If the vas deferens are blocked by cicatricial processes, there will be no semen in the sperm.
- Immune causes
Generally, this is the result of past diseases of the male testicles. If the hematotesticular barrier is damaged, sperm get sperm antibodies. They inactivate sperm, making the ejaculate unsuitable for fertilization.
- External factors
These are alcohol, smoking, drugs, some drugs, industrial poisons, radiation, etc. According to the latest research smoking takes a tremendous impact on fertility.
- Sexual problems
They include anejaculatory phenomenon, retrograde ejaculation. For obvious reasons, it is problematic to conceive a child in the case of erectile dysfunction.
- Idiopathic infertility
Symptoms of male urogenital diseases are absent. After examining a patient, it is not possible to find out why he could not conceive a child. Gradually, the frequency of idiopathic infertility in the world is declining. This is due to the fact that doctors are becoming more and more aware of the causes of impaired fertility.
Screening for Male Diseases
You can be diagnosed in the event of symptoms of male diseases in a clinic. You should be examined by a urologist or a STD specialist. We use modern laboratory tests and instrumental methods in the process of diagnosing diseases. It is important not only to establish a diagnosis, but also to clarify the features of the pathological process in order to select the optimal treatment.
The main diagnostic methods are used:
- microscopic smear on the flora;
- bacteriological culture of urine, urogenital organs or other material;
- prostate secretion microscopy;
- PCR scraping the epithelium for genital infections;
- various tests of urine to assess its quantity, physical characteristics, chemical composition;
- spermogram (ejaculate test);
- Ultrasound of the organs of the scrotum, prostate, kidney, and bladder.
Most male diseases are effectively identified and treated. In case of the detection of inflammatory processes in penis, prostate or testicles, an etiological diagnosis is carried out to find the pathogen. After that, targeted treatment is selected allowing a patient to quickly destroy the infection and get rid of the symptoms of pathology. After completing therapy, doctors re-take tests to confirm cure. This approach avoids the re-development of male diseases in the future.





